Ventricular fibrillation is always pulseless and must be confirmed by ekg or defibrillator monitor. If you’re at risk for ventricular fibrillation and its serious consequences, your doctor may recommend:

Diagnostic workup in patients presenting with sustained
You and your doctor will decide which one is right for you.

Ventricular fibrillation treatment guidelines. Fibrillation is an uncontrolled twitching. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse. This is followed by death in the absence of treatment.
The treatment of ventricular arrhythmias is a major challenge for cardiologists both clinical and interventional ones. These medications include vasopressin and amiodarone, and are given to restore a normal heart rhythm after doctors have used an automatic defibrillator at least three times. Epinephrine is the first drug given and may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes.
It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Short for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, this technique uses chest compressions to force blood throughout your body. Published by canadian cardiovascular society, 05 april 2020.
Vw indicates the vaughan williams classification of antiarrhythmic drugs (95). Treatment of the underlying shd or ischaemia will in most cases not be sufficient to prevent monomorphic vt (mmvt) recurrences. Resume cpr for 2 minutes immediately after defibrillation.
Wide complex tachycardia (wct) is used to define all tachyarrhythmia with qrs complex duration greater than 0.12 seconds. Icd implantation (class i) consider antiarrhythmic therapy with quinidine, programmed electrical stimulation guided or. Depending on the type and severity of your arrhythmia, and the results of various tests including the electrophysiology study, there are several treatment options.
This includes a subset of arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia (vt), ventricular fibrillation (vf), premature ventricular contractions (pvc), and ventricular flutter. 2017 aha/acc/hrs guideline for management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Uab cardiovascular institute delivers optimal patient care for heart rhythm disorders.
Defibrillation is the treatment of choice and should occur as soon as possible. The treatment of (vf and pulseless vt) ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia is included in the cardiac arrest algorithm. However, atrial flutter generally responds less well to drug treatment than atrial fibrillation.
Indication • cardiac arrest patient presenting in ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (icd), which can correct abnormal heart rhythms
2020 canadian cardiovascular society and canadian heart rhythm society position statement on the management of ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation in patients with structural heart disease. Ventricular fibrillation is initially found in about 10% of people with cardiac arrest. Cpr should be started immediately for anyone who doesn’t have a pulse and shouldn’t be stopped until they start breathing normally on their own, an automated external defibrillator.
This position statement focuses on the management of sustained ventricular tachycardia (vt). Treatment recommendations include [ 115] : 2014 aha/acc/hrs guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation.
If the heartbeat is interrupted, even for a few seconds, it can lead to fainting (syncope) or cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation (vf) is a severely abnormal heart rhythm ( arrhythmia) that is life threatening. Arrhythmia medications, which can help control rhythm disturbances;
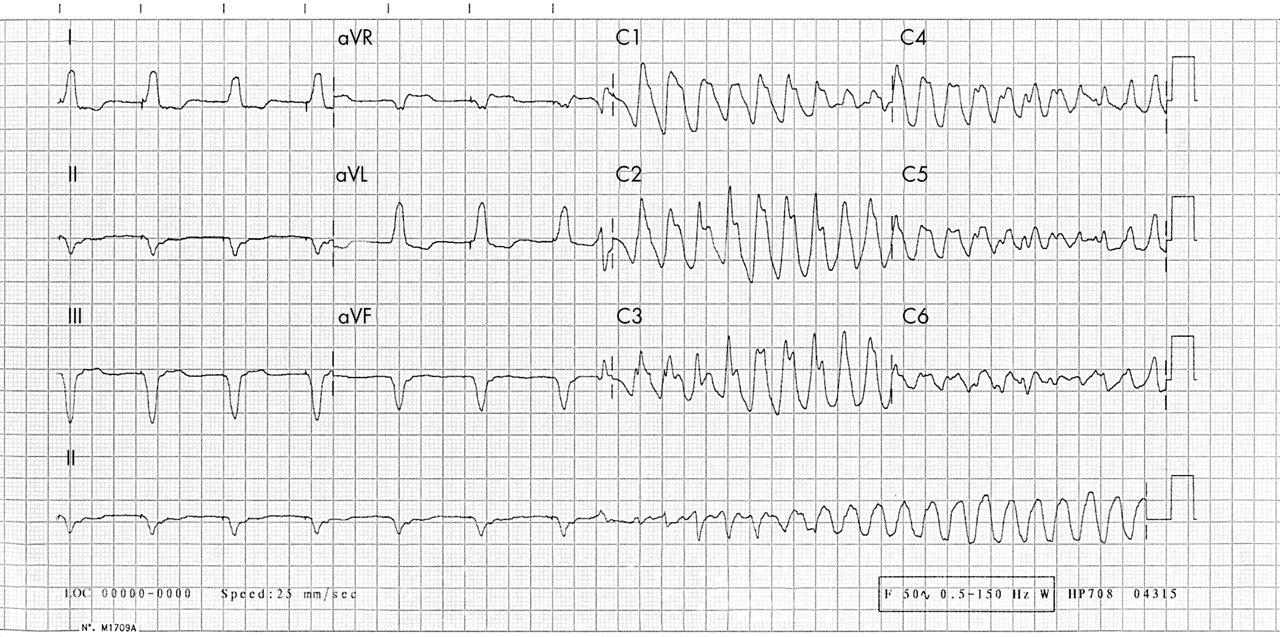
Ventricular fibrillation is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver. The video below shows an example of what ventricular fibrillation will look like when you see it. Vf and pulseless vt are shockable rhythms and treated in similar fashion.
If epinephrine is not effective, the next medication in the algorithm is amiodarone 300 mg. Treatment of vas with aads (amiodarone, mexiletine, or sotalol), catheter ablation, and/or antitachycardia pacing (atp) from an icd should be considered in addition to an icd. This includes a subset of arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia (vt), ventricular fibrillation (vf), premature ventricular contractions (pvc), and ventricular.
2017 acc/aha/hrs guideline for the evaluation and management of patients with syncope. Guidelines summarize and evaluate all available evidence on a particular issue at the time of the writing process, with the aim of assisting health professional Emergency treatments for ventricular arrhythmias include:
In many cases, such as during an electrical storm, the priority is patient stabilization. If the patient remains in ventricular fibrillation, pharmacological treatment should begin. Vf is the most commonly identified arrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients.
Continuously repeat the cycle of (1) rhythm check, (2) defibrillation, and (3) 2. Control of the ventricular rate is usually an interim measure pending restoration of sinus rhythm. Types of proarrhythmia during treatment with various antiarrhythmic drugs for atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter according to the vaughan williams classification.
The heart pumps blood to the lungs, brain, and other organs.
Careful attention to pvc characteristics on surface electrocardiogram has proven useful for the initial localization of the ectopic focus, which may then serve as a guide to procedural planning. They are easily detected on an ekg.

[PDF] Reconstruction of Premature Atrial Contraction and
Also referred to a premature ventricular beats, premature ventricular depolarizations, or ventricular extrasystoles) are triggered from the ventricular myocardium in a variety of situations.

Premature ventricular contractions treatment. A doctor then reviews the data to diagnose premature ventricular contractions. Some will be diagnosed by your doctor as premature ventricular contractions (pvcs). The beat following the early pulse may be uncomfortable or painful.
If you opt for drug therapy, it is usually a good idea to start with a trial of beta blockers—drugs that blunt the effect of adrenaline. Recent efforts have focused on optimizing techniques for mapping and ablation of pvcs in patients with symptoms or reduced lvef. Most often, pvcs that happen only once in a while don't need any treatment.
I have also read, and found to be true, that adding electrolytes can really help. Approach to management of premature ventricular contractions. Watch an animation of a normal heartbeat.
While they may reduce the pvcs themselves, beta blockers work better. Premature ventricular contractions (pvcs) occur when an early electrical pulse and contraction in one of the heart’s lower chambers, the ventricles, disrupt your normal heartbeat. Premature ventricular contractions are frequently encountered and management is determined by symptoms, precipitating factors, and the presence of underlying cardiac disease.
The signal quickly travels down your heart’s conducting system. Your heart has 4 chambers: Infrequently, premature contractions can be caused by disease or injury to the heart.
Premature beats that start in your heart’s upper chambers are premature atrial contractions, or pacs. You probably don't need medical treatment for pvcs if they don't happen often and you don't have other health conditions. Stress can also trigger pvcs.
Catheter ablation has emerged as a safe and effective option for the treatment of frequent pvcs. Increasing age, a taller height, a higher blood pressure, a history of heart disease, performance of less physical activity, and smoking each predict a greater pvc frequency. These cells are in the sinoatrial (sa) node in the right atrium.
They are not effective and only lead to side effects. Pvcs are a common type of abnormal heartbeat. If you have another problem with your heart that's treated, your pvcs may decrease.
For example, you might take a medicine to lower your blood pressure or lower your heart rate. Ecgs demonstrating narrow and wide premature ventricular contractions (pvcs). No specific medical treatment is indicated in asymptomatic pvcs or tolerable symptoms in the absence of cardiac disease;
Premature ventricular contractions, or pvcs, are a type of abnormal heartbeat. This extra heartbeat may feel like a fluttering sensation or like your heart skipped a. A, patient with a narrow left bundle branch/inferior axis pvc.the patient had normal left ventricular (lv) function but was referred because of symptoms of persistent palpitations despite trials of metoprolol and flecainide.
Ablation is another treatment option for some patients with frequent or prolonged pvcs. Stress testing is not necessary and usually, neither is an echocardiogram. There is a better way.
1 beta blockers are not as effective as true antiarrhythmic drugs at eliminating pvcs, but they are generally safe and usually well tolerated. You may need any of the following: Many times, treatment options for pvcs include medication and lifestyle changes, as lifestyle factors can impact pvcs.
Reducing or eliminating these substances can help reduce your premature ventricular contraction symptoms. Caffeine, alcohol, tobacco and other recreational drugs are known triggers of premature ventricular contractions. Don’t waste your time or money.
Your treatment will depend on the cause of your pvcs. Cardiac ablation is a procedure that is used to treat an abnormal heart rhythm. Pvcs are extra electrical impulses arising from one of the cardiac ventricles, usually the left ventricle.
Ask your healthcare provider for more information. Sometimes the presence of pvcs indicates an inherent electrical instability in the heart, and therefore indicates an. After a confirmed diagnosis of pvcs, your physician will discuss treatment options with you.
Normally, a special group of cells begin the signal to start your heartbeat. Premature ventricular contractions (pvcs) have been associated with several medical comorbidities, most of which are modifiable and should be considered either prior to or in conjunction with pharmacologic therapy or interventional procedures. If a reversible cause of pvcs is not determined, reassurance is recommended.
Heart medicine may be given to make your heart beat at a regular rate and rhythm. However, an understanding of the medical treatment options is necessary because medical management is still the first line of therapy. At the cellular level, ventricular myocytes spontaneously depolarise to create an extrasystole ‘out of sync’ with the cardiac cycle.1 the prevalence depends on the characteristics and comorbidities of the population, the method by which the population is.
Other drugs that may be used to treat frequent pvcs include calcium channel blockers and other more potent heart rhythm medications. Reducing or avoiding these substances can reduce your symptoms. For most patients, a prescription beta blocker or calcium channel blocker is the first step in treatment.
Beta blockers are safe and effective drugs that are often used to treat heart arrhythmias. However, do not add them through sugary sports drinks as sugar is also known to cause premature ventricular contractions. Those that start in the lower chambers are premature ventricular contractions, or pvcs.
Premature ventricular complexes (pvcs) are the most common arrhythmias in daily practice. Drinking enough water each day can have a profound effect on reducing and curing pvcs, as well as your overall health. Doctors are quick to prescribe pharmaceuticals for this condition.
2 upper atria and 2 lower ventricles. For example, reducing stress and decreasing caffeine intake could lessen the occurrence of pvcs.
1 they describe specific electrocardiographic characteristics of the new polymorphic. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (cpvt) is an inherited arrhythmia, characterized by polymorphic ventricular tachycardia induced by adrenergic stress.
Bilateral thoracoscopic cervical sympathectomy for the
Unstable polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is treated with unsynchronized shocks (defibrillation).

Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia treatment. If someone is found to be in vt (ventricular tachycardia), treatment typically involves electrical cardioversion/defibrillation (shock) to return the heart rhythm back to normal. The role of medical therapy in the treatment of idiopathic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (ipmvt) and idiopathic ventricular fibrillation (ivf) is not well established. Lessons from one case lampros sioros, md,1 giannis g.
The first line of treatment for catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is treatment through medication. The most common cause of pvt is myocardial ischaemia/infarction. There are several types of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia.
Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (pvt) is a form of ventricular tachycardia in which there are multiple ventricular foci with the resultant qrs complex varying in amplitude, axis, and duration. Successful emergency treatment with intravenous propranolol. The rhythm may be irregular.
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (vt) is a rare arrhythmogenic disorder, which may cause sudden death and whose relationships with mutations in cardiac ryanodine receptor gene have been recently established. Ventricular tachycardia (vt) and ventricular fibrillation (vf) cause approximately 300,000 deaths per year in the united states (us) and account for 5.6% of all mortality. Torsades de pointes) is best treated with intravenous magnesium.
Current medications in use include amiodarone, lidocaine, isoproterenol, verapamil, and quinidine. The key difference between polymorphic and monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is that polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is a type of abnormally fast heart rate with a continuously varying qrs complex morphology in a surface electrocardiogram, while monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is a type of abnormally fast heart rate with uniform qrs. Nadolol, or propranolol if nadolol is unavailable, should be the preferred bb for treating symptomatic children with cpvt.
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (cpvt) is a heart rhythm problem, or arrhythmia.if you have it, your heartbeat is faster and irregular at times. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (pvt) is a type of ventricular tachycardia in which there are several ventricular foci with the resultant qrs complexes differing in amplitude, axis and period. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (cpvt) is an inherited arrhythmogenic disease that can cause sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation (vf).
This is in distinction to acquired long qt, which may be treated with beta stimulation (isopreterenol). Patients with a prolonged qt interval have. A ventricular tachycardia with varying qrs morphology or varying electrical axis is classified as polymorphic.
Defibrillation is used because synchronization is not possible. Patients with the condition will typically be prescribed beta blockers, which need to be taken daily, and work by slowing the heart rhythm and preventing the development of an irregular heartbeat. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is a more organized rhythm than the polymorphic form, and patients may maintain a reasonable hemodynamic state.
Cardiovascular polymorphous ventricular tachycardia has been attributed to methadone [ 63a] and has been treated in one case with left cardiac sympathetic denervation [ 64a ]. Preventive therapy of congenital long qt includes use of beta blockers (same with catecholaminergic pmvt, as in both of these, beta stimulation provokes torsade); Several types of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia have similar electrocardiographic characteristics but have different modes of therapy.
Torsades de pointes (tdp) is a specific form of pvt occurring in the context of qt. In fact, medications considered the treatment of choice for one form of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, are contraindicated for the other. In the absence of hypotension, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia can be treated with intravenous sotalol (1 mg/kg to a maximum of 100 mg) or amiodarone (5 mg/kg).
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia is treated using the left branch of the heart attack arrest algorithm. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is a rare ion channelopathy caused by myocardial ca 2+ dysregulation that can lead to sudden death. 1 vt is considered the most common wide complex tachycardia.
These wide complex tachycardias tend to originate in the ventricles rather than like a normal rhythm which originates in the atria.
Once left ventricular dysfunction occurs a series of compensatory mechanisms are triggered which lead to a host of structural and neurohormonal adaptations. Echocardiography and a pulmonary artery catheter are.

Physiopathology of left ventricular systolic dysfunction
Nevertheless, among the limited data available to address the potential utility of intervening with treatment in patients with alvsd, the studies of left ventricular dysfunction (solvd) prevention trial showed that the use of enalapril in patients with alvsd brings about a significant improvement in mortality and morbidity.

Left ventricular systolic dysfunction treatment. Many recent treatments for heart failure, both pharmacological and pacemaker‐based, have brought about significant improvements in left ventricular systolic function 1 2 3 4.specifically, disease modifying treatments such as β‐blockers 1, 2, aldosterone receptor blockers 14, 15, ace inhibitors 16, angiotensin receptor blockers 17 as well as cardiac. The preferred initial treatment might be: Also, because it potently activates the sympathetic system, lv systolic dysfunction is an even stronger predictor of sudden death than lvh at the.
When treating a patient with diastolic dysfunction, it is important to control the heart rate and prevent tachycardia to maximize the diastolic filling period. Left ventricular systolic function (as assessed by any imaging modality) is a continuum ranging from normal function to severe impairment. Coronary artery disease (cad) is the leading cause of left ventricular systolic dysfunction (lvsd;
Left ventricular systolic dysfunction is common postoperatively and is treated with optimization of preload, maintenance of a high normal heart rate (e.g., with pacing at 90/min), and inotropic support (see chapter 21 ). Ventricular remodelling is the ability. Data from large and small clinical trials reflect major differences in the pathophysiology, treatment, and prognosis of left ventricular (lv) systolic and diastolic dysfunction.
7 left ventricular systolic dysfunction patients report moderate depressed mood (26%) 8 left ventricular systolic dysfunction patients report mild depressed mood (30%) 9 left ventricular systolic dysfunction patients report no depressed mood (34%) what people are taking for it. These studies also indicate that medical therapy can benefit patients with lv dysfunction regardless of whether or not they are symptomatic. Only after a doctor has made a diagnosis, determined the cause and measured the progression of the systolic dysfunction can the patient choose an appropriate treatment option.
Lv systolic dysfunction (lvef less than 40%) was confirmed in all patients by echocardiography (mean ef 26.5±6.9%). Monitor weight and hydration status. We are living in the digital age, when people completely depend on written information:
Left ventricular systolic dysfunction is common postoperatively and is treated with optimization of preload, maintenance of a high normal heart rate (e.g., with pacing at 90/min), and inotropic support (see chapter 21). Early detection and treatment of asymptomatic left ventricular systolic dysfunction give the chance to improve outcomes and to reduce costs due to the management of patients with overt heart failure. Left ventricular systolic dysfunction (lvsd) is the most important predictor of mortality in chagas cardiomyopathy (chcm).
Haemodynamic, neurohormonal, and molecular factors operate to modulate remodelling of the left ventricle and vascular tree (fig 1). The following list of medications are. Use clinical judgement when deciding which medication to start first, e.g.
Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of heart failure due to left ventricular systolic dysfunction (lvsd) within worcestershire. Echocardiography and a pulmonary artery catheter are helpful to. Unfortunately, the diagnosis of lvsd requires advanced diagnostic testing, such as echocardiography (echo), computer tomography,.
67 rows drugs used to treat left ventricular dysfunction. Neurohormonal blockade, now the cornerstone of heart failure therapy, has been shown to have salutatory effects in patients with asymptomatic lv systolic dysfunction, both in reversing. The approach to management of asymptomatic left ventricular systolic dysfunction (alvsd) includes treatment (management of contributing conditions, neurohormonal blockade, and arrhythmia management), avoidance of drugs that may precipitate heart failure (hf), and monitoring for progression.
The goal of therapy is to halt and even reverse lv remodeling. Lvsd must be at least moderate to be the likely cause of their heart failure. The increased survival after acute myocardial infarction induced an increase in heart failure with left ventricular systolic dysfunction.
Systolic blood pressure is the top number when reading blood pressure levels, and generally doctors recommend it be below 140. In more severe cases, your doctor might recommend undergoing a surgical procedure to implant certain medical devices like a defibrillator or a left ventricular assist device in your heart to help. 5 the trandolapril cardiac evaluation.
Left ventricular (lv) hypertrophy (lvh) in hypertensive subjects is associated with several pathophysiological features that promote myocardial electric instability and ventricular arrhythmias. Previously, systemic chemotherapy with anthracyclines and radiation therapy were the only cancer treatments with. Chronic treatment addresses the underlying conditions that led to the hf in the first place.