Acute myeloid leukemia is infamous for being challenging to treat, due to the capability of the cells forming resistance to treatment. Five types of treatment are used:
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Overview Bristol Myers
An eastern cooperative oncology group trial (e4995).,
How to treat acute myeloid leukemia. Though serious for many, especially patients over age 60, aml is treatable and potentially curable for younger people and those with certain disease subtypes. Acute myeloid leukemia (aml) is one of the most common types of blood cancer. The 2 drugs most commonly used are:
These included several targeted therapies like. Patients receive supportive care for side effects of treatment. Specifically, acute myeloid leukemia, which is also known as aml, is considered to be one of the most frequently occurring types of leukemia and is a major cause of mortality in the united states.
If you have the type of aml known as acute promyelocytic leukaemia, you'll usually be given other drugs as well as having chemotherapy. Acute myeloid leukemia (aml) is a clonal disease of hematopoietic progenitor cells that are unable to differentiate [1]. How i treat acute myeloid leukemia.
The treatment of aml usually has two phases. The main treatment for most types of aml is chemotherapy, sometimes along with a targeted therapy drug. Since 2017, nine agents have been approved for various indications in aml.
There are different types of treatment for patients with acute myeloid leukemia. The recent wave of new drug approvals for acute myeloid leukemia (aml) by the fda has resulted in overlapping treatment options, especially in older patients or those considered unfit for intensive chemotherapy and in patients with relapsed or refractory disease.â these therapies are a welcome advance for patients with aml but present physicians with new. Other drugs (besides standard chemotherapy drugs) may be used to treat people with acute promyelocytic leukemia (apl).
Acute myeloid leukemia can be very aggressive. An eastern cooperative oncology group trial (e4995). The acute myeloid leukemia (aml) treatment landscape has changed substantially since 2017.
This formulation strictly follows the principles of ayurveda and is 100 % pure, natural, and is free from preservatives, additives, and fillers. This might be followed by a stem cell transplant. Radiation therapy chemotherapy with stem cell transplant;
The word “myeloid” refers to the type of cells that are cancerous. Myeloid cells are blood cells that develop into many different kinds of immune cells. More than one quarter of a million adults throughout the world are diagnosed annually with acute myeloid leukemia (aml).
Planet ayurveda is offering a best and effective treatment for acute myeloid leukemia such as crab care pack. The acute myeloid leukemia (aml) treatment landscape has changed substantially since 2017. The word “acute” means that the cancer can advance quickly and needs to be treated right away.
This drug was originally designed for lymphoma, but it showed a remarkable effect on acute. I would recommend that if either you or a family member is diagnosed with this to seek out a center of excellence. Natural treatment for acute myeloid leukemia.
Some acute myeloid leukemia with good genetic or molecular profile can be well treated or even cured by current standard intense chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation. How is acute myeloid leukemia treated? Generally it is treated at major clinical centers with a lot of expertise in leukemia especially at first.
Up until 2018, old patients had a bad outcome because of poor regimens and side effects from the effective ones, until the fda approved ventoclax. Progress in the understanding of the biology and therapy of acute myeloid leukemia (aml) is occurring rapidly. As mentioned before, traditional chemotherapy may not be the best option for old individuals suffering from aml.
This article will explain acute myeloid leukemia's survival rate and outlook and highlight the nuances of how they are affected by age, aml type, and treatment response. Aml is seen in both children and adults. Survival rates for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (aml) older than 75 years are still quite dismal.
Not all acute myeloid leukemia can be cured. The current standard of care, based on chemotherapy and allogeneic.
To determine the effect of age, severity of lung disease, severity and frequency of exacerbation, steroid use, choice of an antibiotic, and the presence of comorbidity on the outcome of treatment for an acute exacerbation of copd. For antibiotic treatment of acute exacerbations of copd (aecopd) the national guidelines in denmark recommend either first choice amoxicillin 750 mg tid (amx) or amoxicillin with clavulanic acid 500 mg/125 mg tid (amc).

Algorithm for antibiotic treatment of acute exacerbations
Addition of clavulanic acid offers a broader spectrum;
Copd acute exacerbation treatment. Discuss the initial treatment of acute exacerbations of copd. Care of the hospitalized patient with acute exacerbation of copd patient population: Six studies including 670 participants contributed data on mortality.
One potential approach to a patient with copd and possible pneumonia is the following: Acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) are treated with oxygen (in hypoxemic patients), inhaled beta 2. Treatment of chronic stable copd aims to prevent exacerbations.
Exacerbations involve increased airway inflammation, increased mucus production and increased gas trapping. In chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, a combination of ipratropium and albuterol is more effective than either agent alone. Classification is via gold’s classification (see diagnosis and management of stable copd in ‘related topics’ below).
Identify which patients with an acute exacerbation of copd should receive antibiotics. The evidence was appraised using the grading of Effects of combined treatment with glycopyrrolate and albuterol in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Abstract this document provides clinical recommendations for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) exacerbations. (1) start on antibiotic coverage for pneumonia (e.g. The quality of evidence was low.
‘an acute and sustained worsening of symptoms that require additional treatment’2 •treated with systemic corticosteroids and antibiotics (unselectively) 1. The nhs protocol for management of copd exacerbations in primary care states that bronchodilators and corticosteroids are the mainstay of exacerbation treatment. Explain recent evidence supporting a shorter duration of steroid treatment for acute exacerbations of copd.
Meta‐analysis showed no statistically significant effects of rehabilitation on mortality (pooled or 0.68, 95% ci 0.28 to 1.67). When prescribing an antibiotic for an acute exacerbation of copd, follow table 1 for adults aged 18 years and over. A retrospective chart analysis over 24 months.
Procedure or treatment must be made by the physician in light of the circumstances presented by the patient. A randomized, controlled multicentric study of inhaled budesonide and intravenous methylprednisolone in the treatment on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Copd characterized by the cardinal symptoms of dyspnea, cough, increased sputum purulence and production/volume.
The routine administration of oxygen at high concentrations during a copd exacerbation has been associated with a higher mortality rate than with a titrated oxygen approach. •over 1.5 million gp consultations annually in uk related to exacerbation1 definition: Can be used to guide treatment steps.
7 however, a systematic review of 19 copd guidelines reported that the criteria for treating patients with antibiotics were largely based on an increase in respiratory symptoms, while. Procalcitonin (pct) may be helpful in determining if antibiotics are necessary or the duration of treatment. The goal of therapy when treating a copd exacerbation is to minimize the negative impact of the current exacerbation and prevent future events.
Give oral antibiotics first line if the person can take oral medicines, and the severity of their exacerbation does not require intravenous antibiotics. A person with copd can experience a period when their symptoms are much worse than usual. Older, frail patients and patients with comorbidities, a history of respiratory failure, or acute changes in blood gas measurements are admitted.
Sometimes ventilatory assistance with noninvasive ventilation or intubation and ventilation. Treatment of pneumonic aecopd consists of treating both pneumonia and copd. Firm diagnosis of copd and helps stage copd severity.
Acute exacerbation of copd typically presents with an increased level of dyspnoea, worsening of chronic cough, and/or an increase in the volume and/or purulence of the sputum produced.may represent the first presentation of copd, usually associated with a history of tobacco exposure.treatment includ A university veterans affairs medical center. This is known as an acute exacerbation.
Opposite, amx alone in a higher dose may offer more time above mic. The study found that home‐based telehealth hospitalization was noninferior to conventional hospitalization when the noninferiority margin was set at 20% of the control group's risk of readmission.109 the data suggest that a subgroup of patients with severe copd may be treated for acute exacerbation at home using telehealth, without the physical presence of. Treatment of acute exacerbations involves.
Review intravenous antibiotics by 48 hours and consider stepping down to oral. Mild exacerbations often can be treated on an outpatient basis in patients with adequate home support.
Correct diagnosis and treatment for pulmonary edema, the most common acute. In patients over the age of 65, it comprises 20% of.
Does Ejection Fraction Decrease with Acute Heart Failure
Ahf patients need different levels of care (discharge, observation, ward, icu, etc.) depending on the severity of their condition.
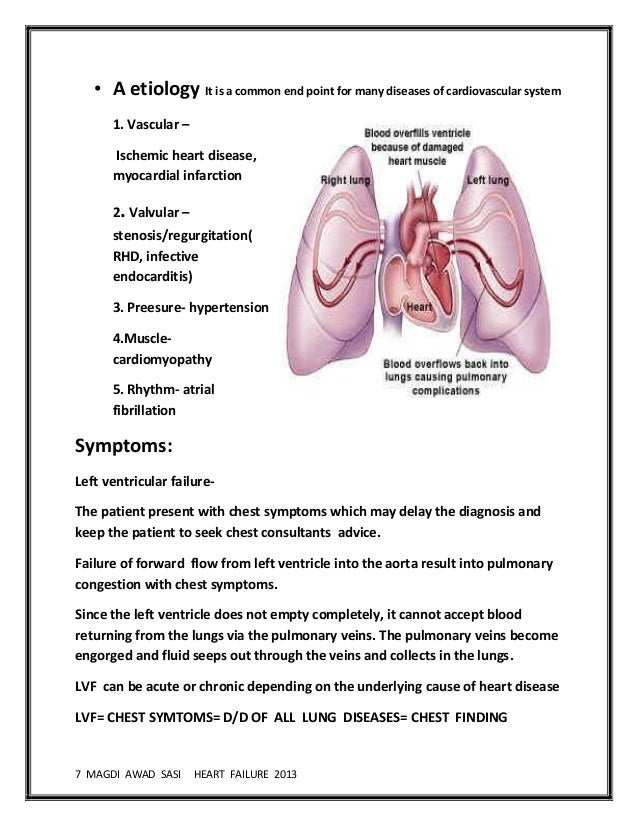
Acute congestive heart failure treatment. 2021 esc guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Prioritize and list ed treatment options for acute exacerbations of congestive heart failure. Heart failure guidelines currently recommend the use of loop diuretics and/or thiazide diuretics to reduce the clinical signs and symptoms of congestion in patients with chronic or acute heart.
Aortic valve stenosis can cause heart failure if the valve cannot open fully. Ideally, an intravenous catheter is placed and furosemide is given iv. Due to these effects, relaxin has been examined as a treatment for acute heart failure.
Blood and imaging tests are also used to diagnose the type of heart failure and to determine how severe it is. According to the random number table method, the patients were divided into 3 groups of 100 patients per group: Determining necessary level of care for acute heart failure patient.
Mcdonagh ta, metra m, adamo m, et al. In this procedure, doctors open up the blocked arteries, allowing the heart muscles’ proper blood flow. Aetiology and diagnosis of heart failure.
Acute congestive heart failure (chf) is one of the most common syndromes encountered in emergency care settings. Medications for acute congestive heart failure nitroglycerin (ntg): De novo acute heart failure.
It affects about 2% of the us population or roughly 4.8 million americans. This guideline covers diagnosing and managing acute heart failure or possible acute heart failure in people aged 18 and over. Acute heart failure is broadly defined as a rapid onset of new or worsening signs and symptoms of hf.
3 treatment options include medication , surgery. Treatment typically includes a combination of medication, surgery, and. 33,34 why does congestion continue.
Tients with acute heart failure were evaluated. Because of the challenges in ahf research, a data imbalance between acute and chronic hf treatment exists as more studies have been performed in the latter. The results of phase i and ii trials have shown favorable clinical trends without any major adverse events, suggesting that relaxin has the potential to be an effective medication for acute heart failure in conjunction with or in place of current treatments.
Heart failure is defined clinically as a syndrome in which patients have symptoms and signs resulting from an abnormality of cardiac structure and/or function. Three hundred patients with acute heart failure were included. Coronary artery bypass graft surgery is the current surgical treatment of chf patients when coronary artery disease is the cause.
The aim of this esc guideline is to help health professionals manage people with heart failure (hf) according to the best available evidence. A small proportion of patients. If the patient is too unstable, furosemide can be administered im and the patient returned to the oxygen cage, pending improvement.
In dogs with a diagnosis of acute congestive heart failure, oxygen should be used in conjunction with a potent loop diuretic, such as furosemide. Treatment for acute heart failure and chronic heart failure is often the same. For many, it is now both preventable and treatable.
This understanding has provided a basis for the management of acute ape, which entails reduction of lv preload, reduction of lv afterload, ventilatory support, inotropic support as needed, and identification and treatment of other underlying factors contributing to elevated lv filling pressures. Airway (a) and breathing (b) oxygen therapy and ventilatory support in acute heart failure The evaluation and treatment of these patients are often best performed in the neonatal or pediatric intensive care unit (icu).
Organic nitrates are available as sublingual tablets, capsules, sprays, patches, ointments or intravenous (iv) solutions, all of which are potent vasodilators. Heart failure is a pathophysiological state in which cardiac output is insufficient to meet the needs of the body and lungs. Fortunately, we now have a wealth of clinical trials to help us select the best management to improve the outcomes for people with hf;
Specifically, congestion takes the form of water retention and. It aims to improve the immediate care of someone who is acutely unwell as a result of heart failure. Congestive heart failure (chf) is one of the most common illnesses treated in the emergency department.
It has been estimated by the american cancer institute that, in 2019, there. Mediastinal irradiation does not seem to clearly improve outcomes, and there is considerable heterogeneity in the central nervous system (cns) prophylaxis strategy used in prospective trials.
Precursor Tcell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia 4.
The complete remission rate was 31%, overall response rate 41%, and os at 1 year was 28%.
T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment. Induction and consolidation chemotherapy alone or in combination with different therapeutic approaches remain the main treatment. An overview of current treatments and novel advances. Because it progresses quickly, treatment needs to begin soon after all is diagnosed.
1 its clinical presentation can include hyperleukocytosis with extramedullary involvement. Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all) treatment options include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplant, and/or targeted therapy. (eds) clinical management of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
The number of new cases being recorded each year is around 1.7 per 100,000 men and women per year. Ad publish your review or original research paper with biomed research international. After performing all of these tests, doctors will have enough information as to what type of leukemia they are facing and any additional alteration they should cover in treatment protocols.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all) treatment regimens. It accounts for ∼20% of all cases of all and is somewhat more common in adults than children, although the incidence diminishes with older age. In arm a, patients with refractory relapse receive a 2 week treatment with mabcampath followed by remission evaluation.
Hindawi's academic journals cover a wide range of disciplines.
Acute attacks of gout are usually treated with either colchicine or high doses of an nsaid (excluding aspirin). Optimal dose of colchicine is still elusive.

Worldwide differences in dose regimens for colchicine in
1.2 mg to 2.4 mg orally daily, administered in 1 or 2 divided doses
Acute gout treatment colchicine. Efficacy of oral colchicine — colchicine for the treatment of gout flares has not been extensively studied in randomized trials even though it was used for centuries for the treatment of a gout flare. Give 500 micrograms of colchicine, two to four times a day, until pain relief is achieved, or diarrhoea or vomiting occurs. Up to 6 days with colchicine 500 micrograms twice a day, or up to 3 days with colchicine 500 micrograms four times a day), and.
Can be given orally, i.m., i.v. Oral colchicine (uncombined with another active ingredient, such as probenecid) was first formally approved by the fda for use in the united states for the. We downgraded the evidence because of a possible risk of selection and reporting biases and imprecision.
1.2 mg at the first sign of flare, then. Do not exceed a total dose of 6 mg of colchicine (i.e. If an acute attack develops during treatment, then the urate lowering therapy should continue at the same dosage and the acute attack treated in its own right.
Start preventative doses 12 hours later. Colchicine is effective but is slower to work than nsaids. Editor—morris et al discussed the use of low dose colchicine in gout.
0.6 mg in 1 hour. 0.6 mg once to twice daily. Moreover, colchicine takes about 24 hours before it is totally cleared in the body.
Colchicine is available in 0.6 mg tablets. For best results colchicine should be started within 24 hours of a gout attack. Therefore, it is way easier for the colchicine to accrue in the body system.
Colchicine appears most effective for acute gout when started in the first 1 to 2 days of the onset of the gout attack. Usual adult dose for familial mediterranean fever usual dose: However, other medications may still be needed for treating pain.
However, subjects have multiple comorbidities that limit the use of some conventional therapies. Acute gout is traditionally treated with nsaids, corticosteroids, and colchicine; Oral corticosteroids, intravenous corticosteroids, nsaids, and colchicine are equally effective in treating acute flares of gout.20 nsaids are.
For the treatment of acute gout flares when taken at the first sign of a flare. This cochrane review is current to august 2020. City hospital, birmingham b18 7qh.
To minimise risk of diarrhoea doses of 500micrograms two to four times daily should be used. They are equally efficacious and comorbidities guide the best choice. The usual dose to prevent gout attacks is:
Colchicine is a medicine for treating inflammation and pain. Anthony r cox, pharmacist (coxar@hotmail.com) author affiliations. The initiation of urate lowering therapy may precipitate an acute attack of gout, and therefore an nsaid or colchicine should be used as a prophylactic during initial urate lowering therapy.
The american college of rheumatology guidelines recommend that nsaids, oral colchicine, or glucocorticoids may all be considered for the treatment of an acute gout flare.3 The usual dose to treat acute gout attacks is: We included four trials (803 randomised participants) in this updated review, including two new trials.
If patient is intolerant of colchicine, prescribe naproxen 250mg twice a day (with ppi) or etoricoxib 30mg once a day (with ppi). A corticosteroid, is an effective treatment in the management of acute gout in patients who cannot tolerate nsaids or are refractory to other treatments. Allopurinol is an effective treatment for reducing concentrations of uric acid.