150mg bd reduced to 110mg bd if. Treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis.
PPT Review of Anticoagulants Unfractionated heparin Low
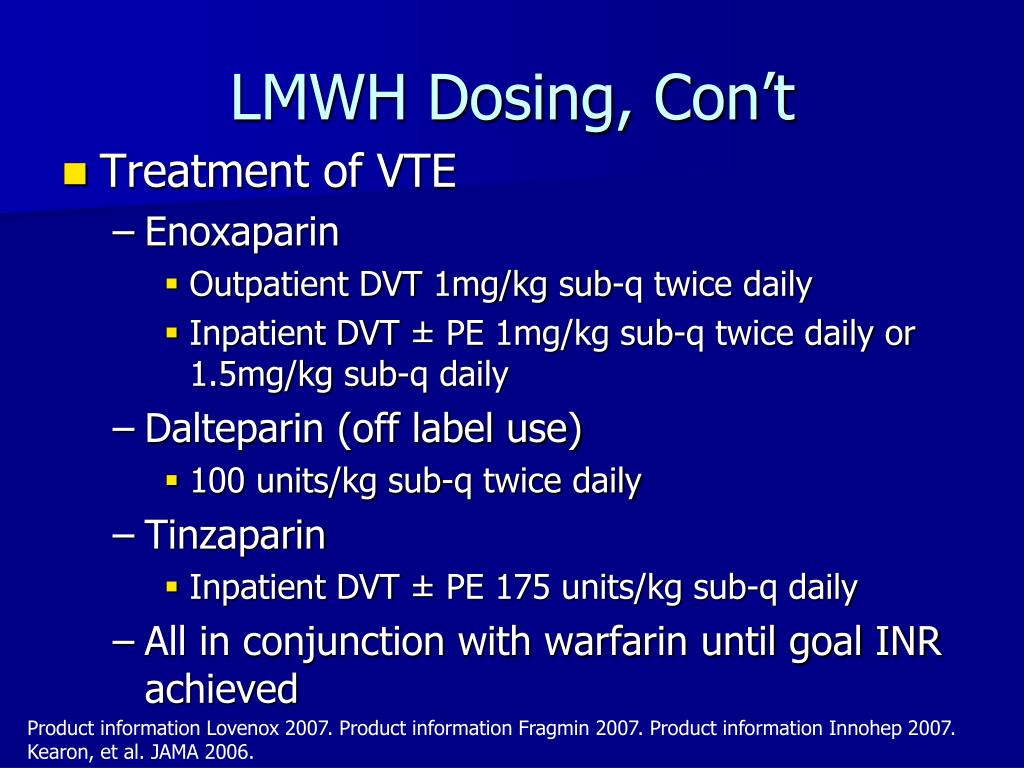
• lovenox 1 mg/kg (maximum dose 120.
Lovenox for dvt treatment. In 2007, the lmwh dalteparin (fragmin) was approved for vte treatment in patients with cancer. Enoxaparin (lovenox) is a lmwh which is effective in both prophylaxis and treatment of deep vein thrombosis (dvt). In canada, dabigatran is approved for the treatment of acute dvt and/or pe after a 5‐10 day initial treatment period with a parenteral anticoagulant (usually a lmwh) and for the prevention of recurrent dvt and pe.
• lovenox 1 mg/kg (maximum dose 150 mg) every 12h (venous thromboembolism) (outpatient or inpatient rx). This prospective, open label randomized multicenter trial randomized 406 patients with active cancer and symptomatic lower extremity deep vein thrombosis (dvt) or symptomatic/incidental pulmonary embolism (pe) to receive rivaroxaban (15mg twice daily for 3 weeks then 20mg once daily) versus. The outpatient treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis without pulmonary embolism when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium
We suggest apixaban as an alternative to lmwh/vka in the acute and short term treatment of vte in appropriately selected patients. Dose and administration of enoxaparin. Treatment of deep vein thrombosis (dvt) andpulmonary embolism (pe), prevention of recurrent dvt pe inadults.
Dalteparin (200 iu/kg daily for 1 month followed by 150. Treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis. Outpatient treatment of acute dvt without pulmonary embolism.
•prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (dvt) in abdominal surgery, hip replacement surgery, knee replacement surgery, or medical patients with severely restricted mobility during acute illness (1.1) •inpatient treatment of acute dvt with or without pulmonary embolism (1.2) The inpatient treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis with or without pulmonary embolism, when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium; The inpatient treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis with or without pulmonary embolism, when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium;
Ad one stop center for thrombosis dr. Not recommended in pe patients who are haemodynamically unstable or may receive thrombolysis. John tan, 20 years in vein care
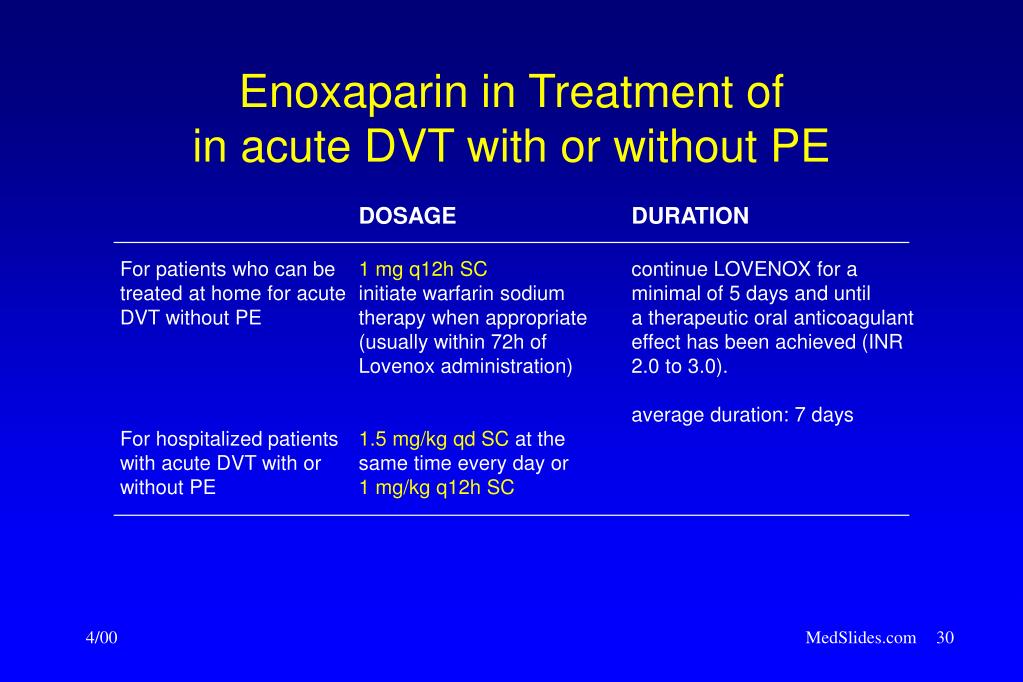
The outpatient treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis without pulmonary embolism when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium Treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis. 150 mg po twice daily for the duration of treatment.
The outpatient treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis without pulmonary embolism when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium • lovenox 1.5 mg/kg (maximum dose 225 mg) qd (venous thromboembolism) (inpatient rx). The inpatient treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis with or without pulmonary embolism, when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium;
Ad one stop center for thrombosis dr. The lmwh agent enoxaparin (lovenox) has no official dosing recommendations for these patients,3 but data in this population suggest that a. Lovenox is a low molecular weight heparin (lmwh) indicated for:
Treatment of deep vein thrombosis with or without pulmonary embolism the recommended dose of lovenox is 1 mg/kg every 12 hours administered subcutaneously in patients with acute deep vein thrombosis without pulmonary embolism, who can be treated at home in an outpatient setting. And serious disease1 that encompasses both deep vein thrombosis (dvt) and pulmonary embolism (pe). John tan, 20 years in vein care