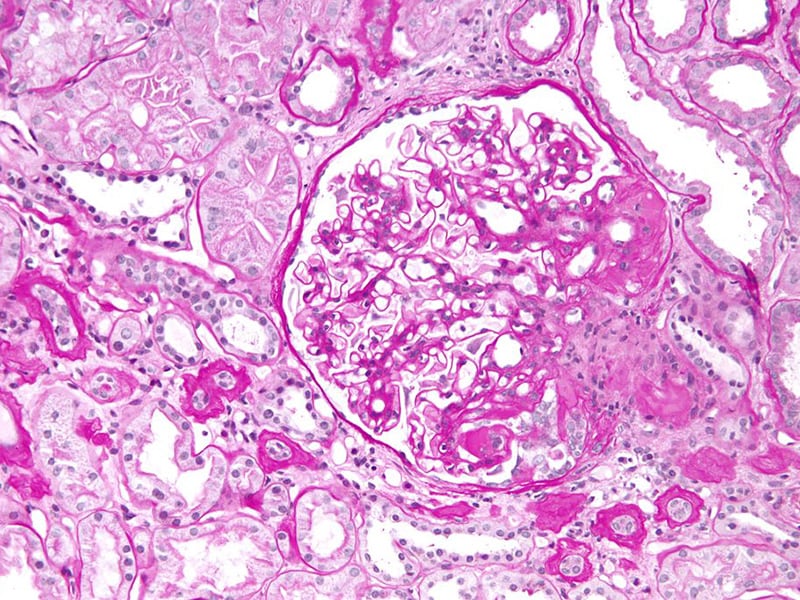
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs): Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis is scattered (segmental) mesangial sclerosis that begins in some but not all (focal) glomeruli and eventually involves all glomeruli.
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) NephCure
Glomeruli are a shallow funnel like stricture, which holds within funnel blood vessels and capillaries.
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis treatment. This information may help your doctor decide what type of treatment is best for you. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) is a leading cause of kidney disease worldwide. Everyone is different and your doctor will make a treatment plan that is right for your type of fsgs.
Use of rituximab (rtx) for focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) and minimal change disease (mcd) is widely described in children. The funnel and its tube filter water, minerals, and metabolites. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) is a histologic lesion, rather than a specific disease entity, that is commonly found to underlie the nephrotic syndrome in adults and children.
However, only about 20% of patients with fsgs experience a partial or complete remission of. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) is a common type of glomerular disease that can lead to chronic renal failure. Up to around 80% of cases of primary fsgs are resistant to steroid treatment.
Secondary form requires treatment of the underlying cause. It is most often idiopathic but may be secondary to use of heroin or other drugs, hiv infection, obesity, sickle cell disease, atheroembolic disease, or nephron loss (eg, in. Fsgs is characterized by the presence of sclerosis in parts (segmental) of at least one glomerulus (focal) in the entire kidney biopsy specimen, when examined.
Usually, treatments for fsgs include: Successful treatment of recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after kidney transplantation by plasmapheresis and rituximab Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the u.s.
Ovid medline, scopus, and cochrane database of systematic reviews were searched. The presumed etiology of primary fsgs is a plasma factor with responsiveness to immunosuppressive therapy and a risk of recurrence after. Corticosteroids remain the mainstay of treatment in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome, including focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs).
When these filters are scarred, they are unable to filter your blood, which can lead to kidney damage and failure. Thus, the approach to a histopathologic. The treatment of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis may be different for different patients because it largely depends on the cause of the disease.
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis is associated with glomerular podocyte damage and foot process effacement, and it is likely that the pattern of fsgs seen on biopsy represents a common pathway for a number of distinct entities with different pathogenetic mechanisms and clinical courses (box 18.2). Some of the treatments for managing fsgs include: The heterogeneity of pathogenesis underlying the lesion must be taken into account in deciding on an appropriate therapy the treatment must be personalized
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) is a nephrotic syndrome. Diuretic medications to help your body get rid of salt and water, which can improve blood pressure and swelling. Treatment of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) can be divided into nonspecific and specific treatment.
Patients who are resistant or intolerant to steroids are treated with immunosuppressive therapy with calcineurin inhibitors (cni), mycophenolate mofetil, or rituximab. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) is a rare disease that affects the filters in your kidneys. Medication to suppress the immune system if you have primary fsgs.
Clinical evidence in adults is limited. Axioms to remember fsgs is a light microscopic lesion (a “pattern of injury”), not a disease. Secondary form requires treatment of the underlying cause.
Glucocorticoids (daily or every other day) are the first line of treatment in children and adults with focal segmental glomerular sclerosis (fsgs). Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) is a morphologic pattern of glomerular injury primarily directed at the glomerular visceral epithelial cell (the podocyte) and defined by the presence of sclerosis in parts (segmental) of some (focal) glomeruli by light microscopy of a kidney biopsy specimen. Various therapeutic regimens have been used in nephrotic fsgs patients.
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) is the scarring or hardening of the glomeruli and the blood vessels of the kidneys. A few case series and small studies have reported mixed results with the use of rituximab for this indication. Corticosteroids (mostly called ‘steroids’), diuretics, immunosuppressive drugs, ace inhibitors and arbs, plasmapheresis, and dietary changes.
The objective of this study was to determine the treatment outcomes of rtx in adults with fsgs and mcd. These drugs, including corticosteroids, may stop the immune system from attacking the glomeruli and further damaging kidney function. The type of treatment you get depends on the cause.
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (fsgs) 1. The effect of treatment with prednisolone alone or its combination with azathioprine and cyclosporin and parameters. Treatment for fsgs focuses on treating the symptoms and preventing any additional scarring.