Unlike other svts, atrial tachycardia does not depend upon the atrioventricular junction or accessory pathways for initiation or maintenance. The doctor may try to stop the episode by gently massaging an area in the neck called the carotid sinus.
Heart pathology. (Subject 13) презентация онлайн
If an episode occurs during an office visit to the doctor then an injection of tambocor may restore the heart rate back to normal.
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia treatment. The majority of attacks are recurrent, brief,. Treatment of paroxysmal tachycardia junctional tachycardia usually heals on its own after a few hours at the most. Treatment for multifocal atrial tachycardia includes:
When paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (pat) strikes, the person may suffer from chest pain or a panic attack. Or a cardiologist to get pat treated. Considering taking medication to treat paroxysmal atrial tachycardia?
The most common way to treat atrial fibrillation is with drugs that control your heartbeat. Medications to treat paroxysmal atrial tachycardia: Ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation treatments:
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (psvt) treatments: Problems typically begin in those 12 to 45 years old. Stopping medicines, such as theophylline, which can increase.
Another common way to treat atrial tachycardia is ablation. If you experience common episodes of atrial tachycardia and all other treatment options are vain, your doctor may suggest implantation of a small device called a pacemaker to deliver electrical impulses that kindle your heart to beat at a normal rate. Atrial fibrillation (af) is a subtype of svt that causes an irregularly irregular heart rhythm.
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia is one of the types of heart disease or arrhythmia an irregular heartbeat. At the time of the crisis, you can also stop using techniques called “vagal maneuvers” or with a drug, the striatum. It is a combination of 3 words.
Doctors may instead suggest avoiding caffeinated beverages and keeping a log of occurrences. If you have a condition that can lead to multifocal atrial tachycardia, that condition should be treated first. When it occurs often, doctors look for cause, and ways to treat it.
If paroxysmal atrial tachycardia occurs rarely, the condition may not be treated. Massages or maneuvers your provider does in an office visit. The various technics and drugs useful in the management of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia have been reviewed from the pertinent literature with an appraisal added based upon personal experiences.
Your doctor may recommend treatment or medications if your episodes occur often or last for a considerable length of time. Drugs used to treat atrial tachycardia the following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition. There are many options but without skilled medical help you won't be able to treat it.
Atrial tachycardia (at) is a type of abnormal heart rhythm, or arrhythmia.it occurs when the electrical signal that controls the heartbeat starts from an unusual location in the upper chambers (atria) and rapidly repeats, causing the atria to beat too quickly. This is where certain areas of the heart are treated to stop them from improperly conducting electricity. Briefly hold the nose and mouth closed and breathe out, or by bearing down, as though straining at a bowel movement.
Accurate diagnosis of the tachycardia by electrocardiographic technies in every patient is emphasized. The doctor may suggest that during an episode of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia the following practice may help. Otherwise synchronized cardioversion is the treatment.
Normal (unless associated with aberrant ventricular conduction). Future episodes can be prevented by catheter ablation. Av nodal reentrant tachycardia, and atrial tachycardia.
How can i treat paroxysmal atrial tachycardia? Paroxysmal which means that the arrhythmia begins and suddenly ends, atrial means that arrhythmia begins in the upper chambers of the heart and tachycardia means that the heart starts beating abnormally fast. This form of pharmacological treatment is for those patients who frequently have episodes of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia and the above mentioned maneuvers are of little to no benefit.
Adenosine is also the first line treatment for patients with paroxysmal atrial tachycardia. May conduct to ventricles 1:1, or 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 into the presence of a block. Drinking less alcohol or caffeine.
May be normal, abnormal, or not measurable. Atrial or supraventricular tachycardia treatments: See online data supplement 7.
Intravenous metoprolol 229 or verapamil 232,233 can be useful for acute treatment in patients with mat. Treatment of atrial tachycardia depends on the severity of your condition and the things that trigger it. Examples of svt include atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation (af), atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (avnrt), also known as paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (psvt), atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (avrt), and multifocal atrial tachycardia (mat).
Select drug class all drug classes calcium channel blocking agents (1) cardiac stressing agents (1) group iv antiarrhythmics (1) group v antiarrhythmics (1) You may be able to temporarily slow your heart rate by holding your breath and straining, dunking your face in ice water, or coughing. Giving magnesium or potassium through a vein;
This is very helpful at stopping focal atrial tachycardia and can also stop reentry problems by blocking part of a faulty electrical circuit. Below is a list of common medications used to treat or reduce the symptoms of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia. Catheter ablation for the treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
Most people take a medication called digoxin (lanoxin). Women are more often affected than men. Atrial tachycardia is a form of supraventricular tachycardia (svt) usually seen in patients with structural heart abnormalities but can be seen in patients with structurally normal hearts.
Recommendations for acute treatment of multifocal atrial tachycardia. Most people with pat don’t need treatment for their condition. About 2.3 per 1000 people have paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
1 doctor answer • 2 doctors weighed in.
1 they describe specific electrocardiographic characteristics of the new polymorphic. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (cpvt) is an inherited arrhythmia, characterized by polymorphic ventricular tachycardia induced by adrenergic stress.
Bilateral thoracoscopic cervical sympathectomy for the
Unstable polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is treated with unsynchronized shocks (defibrillation).

Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia treatment. If someone is found to be in vt (ventricular tachycardia), treatment typically involves electrical cardioversion/defibrillation (shock) to return the heart rhythm back to normal. The role of medical therapy in the treatment of idiopathic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (ipmvt) and idiopathic ventricular fibrillation (ivf) is not well established. Lessons from one case lampros sioros, md,1 giannis g.
The first line of treatment for catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is treatment through medication. The most common cause of pvt is myocardial ischaemia/infarction. There are several types of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia.
Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (pvt) is a form of ventricular tachycardia in which there are multiple ventricular foci with the resultant qrs complex varying in amplitude, axis, and duration. Successful emergency treatment with intravenous propranolol. The rhythm may be irregular.
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (vt) is a rare arrhythmogenic disorder, which may cause sudden death and whose relationships with mutations in cardiac ryanodine receptor gene have been recently established. Ventricular tachycardia (vt) and ventricular fibrillation (vf) cause approximately 300,000 deaths per year in the united states (us) and account for 5.6% of all mortality. Torsades de pointes) is best treated with intravenous magnesium.
Current medications in use include amiodarone, lidocaine, isoproterenol, verapamil, and quinidine. The key difference between polymorphic and monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is that polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is a type of abnormally fast heart rate with a continuously varying qrs complex morphology in a surface electrocardiogram, while monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is a type of abnormally fast heart rate with uniform qrs. Nadolol, or propranolol if nadolol is unavailable, should be the preferred bb for treating symptomatic children with cpvt.
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (cpvt) is a heart rhythm problem, or arrhythmia.if you have it, your heartbeat is faster and irregular at times. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (pvt) is a type of ventricular tachycardia in which there are several ventricular foci with the resultant qrs complexes differing in amplitude, axis and period. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (cpvt) is an inherited arrhythmogenic disease that can cause sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation (vf).
This is in distinction to acquired long qt, which may be treated with beta stimulation (isopreterenol). Patients with a prolonged qt interval have. A ventricular tachycardia with varying qrs morphology or varying electrical axis is classified as polymorphic.
Defibrillation is used because synchronization is not possible. Patients with the condition will typically be prescribed beta blockers, which need to be taken daily, and work by slowing the heart rhythm and preventing the development of an irregular heartbeat. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is a more organized rhythm than the polymorphic form, and patients may maintain a reasonable hemodynamic state.
Cardiovascular polymorphous ventricular tachycardia has been attributed to methadone [ 63a] and has been treated in one case with left cardiac sympathetic denervation [ 64a ]. Preventive therapy of congenital long qt includes use of beta blockers (same with catecholaminergic pmvt, as in both of these, beta stimulation provokes torsade); Several types of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia have similar electrocardiographic characteristics but have different modes of therapy.
Torsades de pointes (tdp) is a specific form of pvt occurring in the context of qt. In fact, medications considered the treatment of choice for one form of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, are contraindicated for the other. In the absence of hypotension, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia can be treated with intravenous sotalol (1 mg/kg to a maximum of 100 mg) or amiodarone (5 mg/kg).
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia is treated using the left branch of the heart attack arrest algorithm. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is a rare ion channelopathy caused by myocardial ca 2+ dysregulation that can lead to sudden death. 1 vt is considered the most common wide complex tachycardia.
These wide complex tachycardias tend to originate in the ventricles rather than like a normal rhythm which originates in the atria.
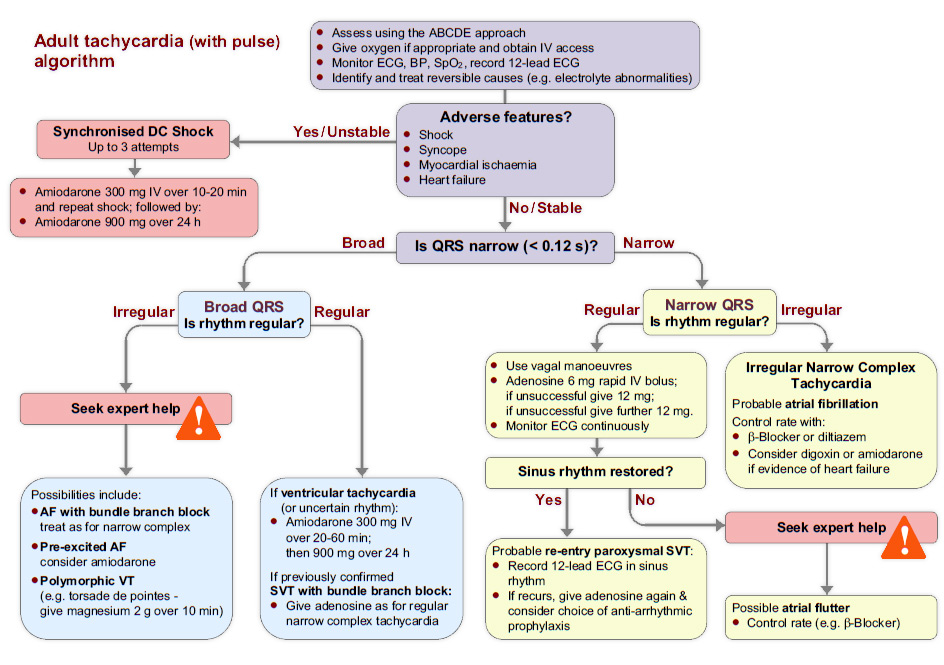
Acute care of narrow qrs tachycardia is guided by the acls algorithm. Prepare for synchronized cardioversion at 0.5 to 1 j/kg, this can be increased to 2 j/kg if the first dose is not effective.
Conference Notes 852015 — ACMC EM
Safety of adenosine in treatment of tachycardia.
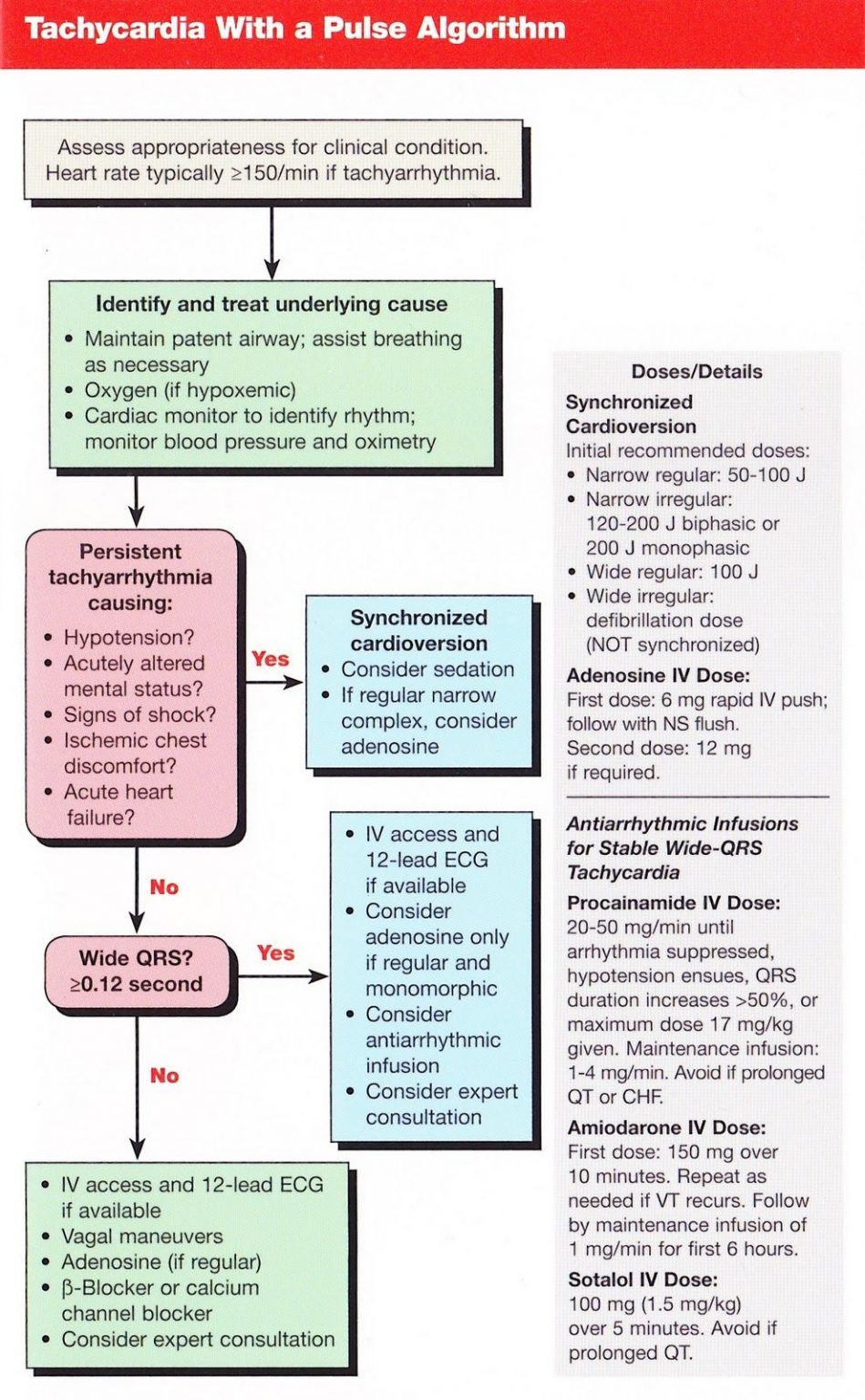
Narrow complex tachycardia treatment. Avoid if prolonged qt or chf. Furthermore, the regular rhythms can be broken down into “av nodal dependent” and “av nodal independent” rhythms, which can help us remember the treatments as well. In this situation atrial fibrillation is the most likely rhythm.
Is the qrs complex normal/narrow or wide? Pediatric narrow complex tachycardia electrical and medication treatments in this protocol are not intended to treat tachycardia that is secondary to underlying conditions (i.e., dehydration, trauma toxins). Consider sedation for cardioversion as long as it does not cause a delay.
But you may need treatment in hospital if you keep having long episodes. Diagnosis for narrow complex tachycardia. Tachycardia with a pulse algorithm
In the clinical setting, the distinction between narrow and wide complex tachycardia (supraventricular vs. 4 af can be triggered by acute alcohol intoxication, thyrotoxicosis, sepsis or dehydration. It is a useful diagnostic tool as well as a treatment in the setting of a narrow complex tachycardia.
If a patient shows signs of immediate danger (systolic blood pressure below 90 mm/hg, loss of consciousness, confusion, or only able to find a carotid pulse), synchronized cardioversion is. Treating supraventricular tachycardia (svt) in hospital. It can also usually be used safely in asthmatics unless they have brittle severe asthma
Applies to all ages unless stated otherwise. When tachycardia has a narrow qrs complex, it's much easier to diagnose it as supraventricular tachycardia. Adenosine is a purine nucleoside that, administered intravenously, causes transient complete av node blockade.
3 patients of older age are at increased risk of developing af, as well as patients with hypertensive, valvular and ischaemic heart disease. Arises almost always as a physiologic response or compensation to an underlying trigger, and this must be identified In stable patients, adenosine is a very important tool in both treatment of certain svts and diagnosis.
Tachycardia with a pulse & adequate perfusion. Sotalol 100 mg (1.5 mg/kg) over 5 minutes It is important to use an approach when assessing a narrow qrs tachycardia:
Ventricular) is fundamental since they are treated differently. The one that i find the most useful is breaking them into regular and irregular rhythms. The topic always comes up of sedation.
It affects women more commonly than men. There are several different ways to break down the differential for narrow complex tachycardia. It may also be administered, with care, to persons with regular wide complex tachycardias if it is likely that the tachycardia is not a.
Consultation with online medical control should be considered for complex patients in whom the cause of the arrhythmia is not obvious. Adenosine can be administered safely to all individuals with narrow complex tachycardia. In the absence of adverse features immediate treatment options include:
Identify the svt type using the differential diagnosis in the american college of cardiology (acc) narrow qrs complex svt algorithm. If the qrs is narrow and the rhythm is irregular, you are dealing with irregular narrow complex tachycardia. Adenosine remains the treatment of choice for terminating most types of regular narrow qrs complex tachycardias except those due to sinus tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, fibrillation, or flutter.
Narrow complex tachycardias are supraventricular tachycardias, meaning only that they originate above the ventricles. Regular narrow complex tachycardia can be treated with: Clinical quality & patient safety.
Svt is rarely life threatening. If the tachycardia has a wide qrs (>0.08 seconds) and the child has a pulse, treat for ventricular tachycardia. Atrial tachycardia (unifocal/multifocal) atrial fibrillation;
A heart rate of 150 should make you suspect atrial flutter is present. Tachycardia can be classified as narrow complex qrs (≤ 0.09 sec) or wide complex qrs (> 0.09 sec.) there are two algorithms used in the treatment of pediatric tachycardia: Adenosine is safe in pregnancy;
Amiodarone 150 mg iv over 10 minutes, or; Clinical presentation and treatment are very similar with the exception of a broad complex tachycardia arising from an avrt. Applies to queensland ambulance service (qas) clinical staff.
Click to view, and click again to close the diagram. Svt is a common cardiac dysrhythmia, affecting people of all ages, often starting at a young age. Broad complex tachycardias should be considered separately.
Describe the ecg, present a differential diagnosis and then narrow the differential. Most have a narrow qrs complex, although, occasionally, electrical conduction abnormalities may produce a wide qrs complex that may mimic ventricular tachycardia (vt). Narrow complex tachycardias are a common clinical problem and can be divided into those in which the arrhythmic circuit is located exclusively in the atrium (pharmacologic treatment is oriented toward altering atrial electrophysiologic properties) and those that involve the av node or an accessory pathway (pharmacologic therapy is directed toward slowing conduction or.