One type of medication used to treat pulseless ventricular tachycardia is a vasopressor, which produces vasoconstriction and increases blood pressure. The word, ventricular, is a rapid heart rate that is started electrically by the ventricles or lower chambers in the heart, which remains in comparison to the common control center within the atria.
Acls Tachycardia Algorithm Pulseless Ventricular
Considering this, do you shock pulseless v tach?

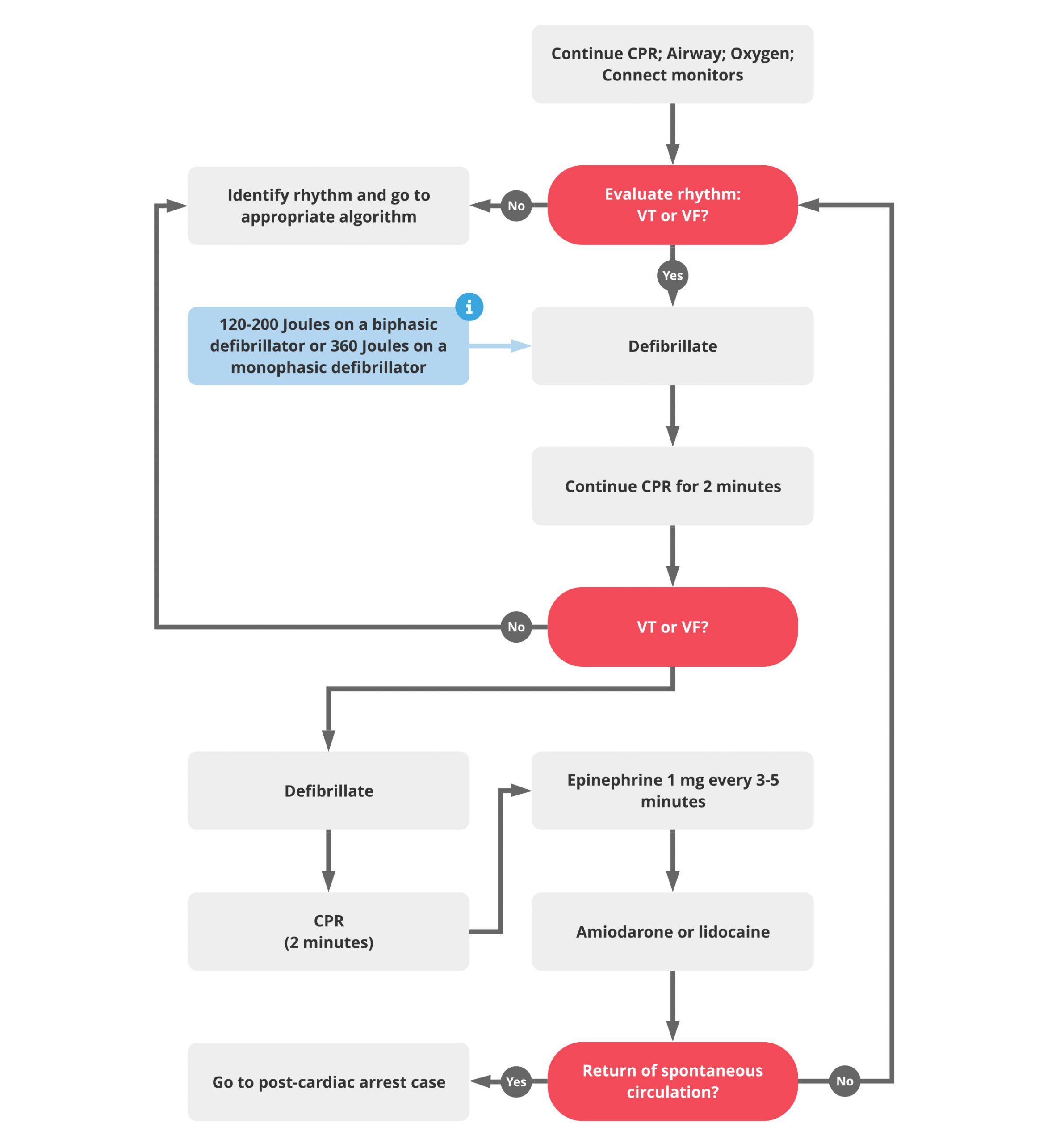
Pulseless v tach treatment. Shocks should only be delivered for vf and pulseless vt. Drugs used to treat ventricular tachycardia the following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition. Pulseless vt, in contrast to other unstable vt rhythms, is treated with immediate defibrillation.
Click below to view the cardiac arrest algorithm diagram. Amiodarone 300mg (following 3rd shock) exclude reversible causes (4 h’s and t’s) clinically compromised Manual chest compressions are administered in order to simulate functional heartbeats and.
Vf and pulseless vt are shockable rhythms and treated in similar fashion. Turn the rate to 70 beats per minute or their intrinsic rate; This is the primary reason you should not use an aed in someone with a palpable pulse.
The treatment of (vf and pulseless vt) ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia is included in the cardiac arrest algorithm. Pals ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia rosc occurs *treatable causes of arrest: Thus, the acls provider must read and analyze the rhythm.
Ventricular fibrillation is the most common initial dysrhythmia in cardiac arrest and will regress to asystole if not treated right away. Pulseless ventricular tachycardia is treated using the left branch of the cardiac arrest algorithm. Ventricular tachycardia is a poorly perfusing rhythm;
Ventricular tachycardia is a rapid heart beat initiated within the ventricles, characterized by 3 or more consecutive premature ventricular beats. Vf and pulseless vt are shockable rhythms and treated in similar fashion. Place defibrillator in pacemaker mode.
Patients may present with or without a pulse. That treatment includes rapid defibrillation. Considering this, do you shock v tach without a pulse?
Hypovolemia toxins hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) h+ (acidosis) tension pneumothorax hypoglycemia thrombosis (mi, pe) hypo/hyperkalemia Vasoconstriction is important during cpr because it will help increase blood flow to the brain and heart. Several misunderstandings are common when discussing details of treatment.
Ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia date: Medical treatment of pulseless vt usually is carried out along with defibrillation and includes intravenous vasopressors and antiarrhythmic drugs. Amiodarone is the most studied drug and is used for the prevention of sudden cardiac death.
Give epi 1mg if (shock + 2min of cpr) fails to convert the rhythm. Acls responses to vf and pulseless vt within a hospital will likely be conducted using a cardiac monitor and a manual defibrillator. When finished click again to close the diagram.
Cpr with minimal interruption (30:2, with 2 minute cycles) intubation; Many tachyarrhythmias of a rate >150 will deteriorate into pulselessness if timely treatment is not given. Give antiarrhythmic if (2nd shock + 2min of cpr) again fails.
The immediate response to an adult patient with tachycardia and a palpable pulse is. Tachycardia is a quick heart rate of more than 100 beats in a minute. Treatment of unstable / pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
To maintain an open airway; Treatment of pulseless ventricular tachycardia is an emergency procedure commonly referred to as a code. Medications to slow the heart rate is another treatment option for patients with ventricular tachycardia.
If a pulse cannot be felt after palpating for up to 10 seconds, move immediately to the acls cardiac arrest vtach and vfib algorithm to provide treatment for pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Vfib is the most common initial dysrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients and will regress to asystole if it isn't treated in a short amount of time. Unstable svt or vt require emergency countershock.
Epinephrine is primarily used for its vasoconstrictive effects. The last term, pulseless, refers to the lack of a pulse, which indicates the. The effective ingredients in vasopressors are vasopressin and epinephrine.
Ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia are treated using the left branch of the cardiac arrest arrest. Pulseless ventricular tachycardia is a temporary condition wherein the heart's large ventricles are pumping very rapidly but completely ineffectively. Currently, the acls protocol for v fib and pulseless v tach recommends that epinephrine be given after the second defibrillation.
Epinephrine can be replaced by vasopressin given 40 units iv once. These drugs can be effective but are associated with some serious, potentially fatal side effects, and they are not used as much as they were in the past. Pulseless arrest treatment the treatment for ventricular fibrillation is rapid […]
The initial shock dose on a biphasic defibrillator. 1 mg of epinephrine iv should be given every 3 to 5 minutes. Turn the miliampules (ma) to 70
The vasopressor that is used for the treatment of vf/pulseless vt is epinephrine.
It is associated with digitalis toxicity or. In addition, a patient with shock resistant unstable vt should receive amiodarone 300 mg iv with a second bolus of 150 mg iv.
Can be monophoric or polymorphic;

Polymorphic v tach treatment. If the patient has runs of polymorphic vt punctuated by sinus rhythm with qt prolongation. Ventricular tachycardia can be classified in a variety of ways. (1) va termination, (2) evaluation and treatment of potential va causes, (3) acute (medical treatment) and chronic (interventional treatment using catheter ablation) prevention of recurrence and (4) treatment of.
Polymorphic vt in patients with a normal qt interval is treated in the same manner as monomorphic vt. Defibrillation is used because synchronization is not possible. Torsades de pointes (tdp) is a specific form of pvt occurring in the context of qt.
The most important treatment is revascularization therapy. If recurrent vt occurs, continue to electrically cardiovert. These wide complex tachycardias tend to originate in the ventricles rather than like a normal rhythm which originates in the atria.
Ventricular tachycardia is a fast heart rate arising from the lower chambers of the heart. An episode that lasts more than 30 seconds, even without symptoms, also needs to be treated. Posts about multifocal ventricular tachycardia written by dr s venkatesan.
Defined as ventricular tachycardia with varying qrs amplitude. However, in most patients there is no clear vf trigger to target, and therefore polymorphic vt or vf cannot be adequately treated with catheter ablation. Pulseless ventricular tachycardia is a medical emergency.
Polymorphic vt in the setting of a normal qt interval is most often associated with acute cardiac ischemia. Pending revascularization, suppression of the dysrhythmia can be attempted with lidocaine or amiodarone. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is a more organized rhythm than the polymorphic form, and patients may maintain a reasonable hemodynamic state.
If blood pressure falls below normal, a person will need electric cardioversion (shock) immediately. Ventricular tachycardia (vtach) treatment for ventricular tachycardia include: In certain clinical settings, ventricular fibrillation (vf) episodes that have premature ventricular contraction triggers can also be targeted with catheter ablation.
Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (polyvtach) rhythm video by the acls certification institute. Monomorphic vt and polymorphic vt is one such classification based on vt morphology.polymorphic vt generally conveys a meaning of origin from multiple focus.but in reality bulk of the polymorphic vt originate from a single focus. Ventricular fibrillation (vfib) treatment for ventricular fibrillation include:
Treatment of the underlying shd or ischaemia will in most cases not be sufficient to prevent monomorphic vt (mmvt) recurrences. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia may be caused by several etiologies (e.g., congenital qt prolongation, acquired qt prolongation, ischemia, takotsubo's cardiomyopathy). Unstable polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is treated with unsynchronized shocks (defibrillation).
Although a few seconds may not result in problems, longer periods are dangerous; The most common cause of pvt is myocardial ischaemia/infarction. Torsades de pointes) is best treated with intravenous magnesium.
To view more videos, check out the acls certification inst. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (pvt) is a form of ventricular tachycardia in which there are multiple ventricular foci with the resultant qrs complex varying in amplitude, axis, and duration. Treatment of vas with aads (amiodarone, mexiletine, or sotalol), catheter ablation, and/or antitachycardia pacing (atp) from an icd should be considered in addition to an icd.
Polymorphic vt/vf may be related to reversible causes as well as genetically determined arrhythmia syndromes and a specialized treatment pathway may be chosen: And multiple episodes over a short period of time is referred to as an electrical storm. Enhanced automaticity (ectopic pacemaker activity) enhanced trigger activity;
It is a rare but important indicator of ongoing ischemia. This is commonly referred to as torsade de pointes, but it's actually not the same thing. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (cpvt) is a heart rhythm problem, or arrhythmia.if you have it, your heartbeat is faster and irregular at times.
Patients with a prolonged qt interval have. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, or chest pain. In the absence of hypotension, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia can be treated with intravenous sotalol (1 mg/kg to a maximum of 100 mg) or amiodarone (5 mg/kg).
Torsades de pointes is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia that occurs in the setting of a long qt interval and appears as waxing and waxing qrs amplitude on ecg. Any episode of ventricular tachycardia that causes symptoms needs to be treated. The key difference between polymorphic and monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is that polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is a type of abnormally fast heart rate with a continuously varying qrs complex morphology in a surface electrocardiogram, while monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is a type of abnormally fast heart rate with uniform qrs.
